Monocrystalline Panels
Monocrystalline and polycrystalline solar panels are two of the most common types of photovoltaic panels used in solar energy systems. While both types harness the sun’s energy to generate electricity, there are distinct differences in their construction, performance, and efficiency.
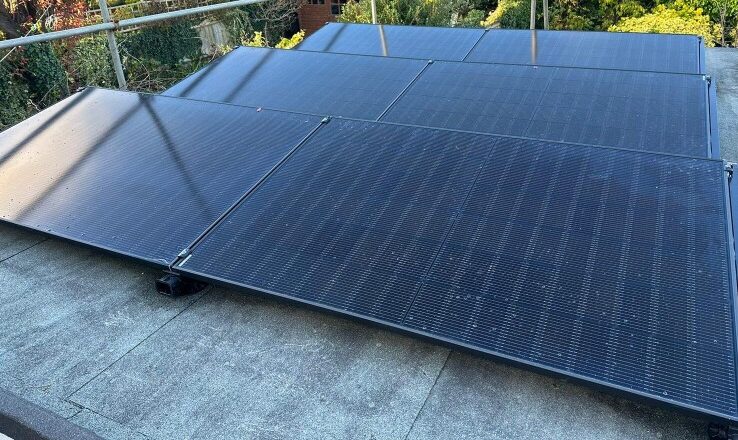

Monocrystalline Solar Panels on a flat roof
How Monocrystalline Panels Work:
Monocrystalline solar panels are made from single-crystal silicon ingots, which are produced by melting high-purity silicon and then growing a large cylindrical ingot from the molten material. The ingot is then sliced into thin wafers, which are used to manufacture individual solar cells. These cells are typically dark black in colour and have a uniform appearance due to their single-crystal structure.
When sunlight hits the surface of a monocrystalline solar cell, photons (particles of light) are absorbed by the silicon material, exciting electrons and creating an electric current. Metal contacts on the top and bottom of the cell collect this current and channel it into wires, where it can be used to power electrical devices or stored in batteries for later use.
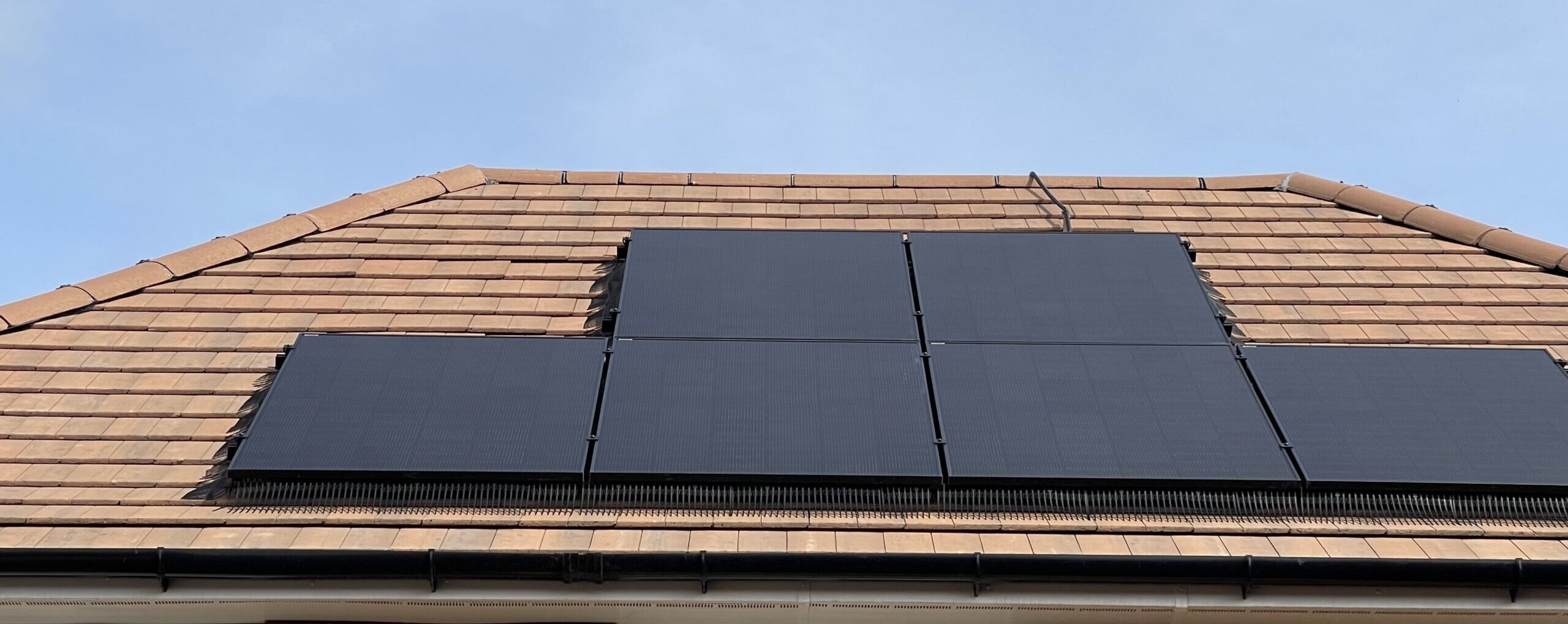

Monocrystalline Solar Panels on a pitched roof
Advantages of Monocrystalline Panels:
- High Efficiency – Monocrystalline panels are known for their high efficiency, meaning they can convert a greater percentage of sunlight into electricity compared to polycrystalline panels. This is due to their uniform crystal structure, which allows for more efficient electron movement within the cells.
- Space Efficiency – Monocrystalline panels typically have a higher power output per square foot compared to polycrystalline panels. This means that fewer monocrystalline panels are needed to achieve the same energy production, making them a good choice for installations with limited roof space.
- Longevity – Monocrystalline panels are known for their durability and longevity. They are often backed by extensive warranties and can last upwards of 25 years or more with proper maintenance.
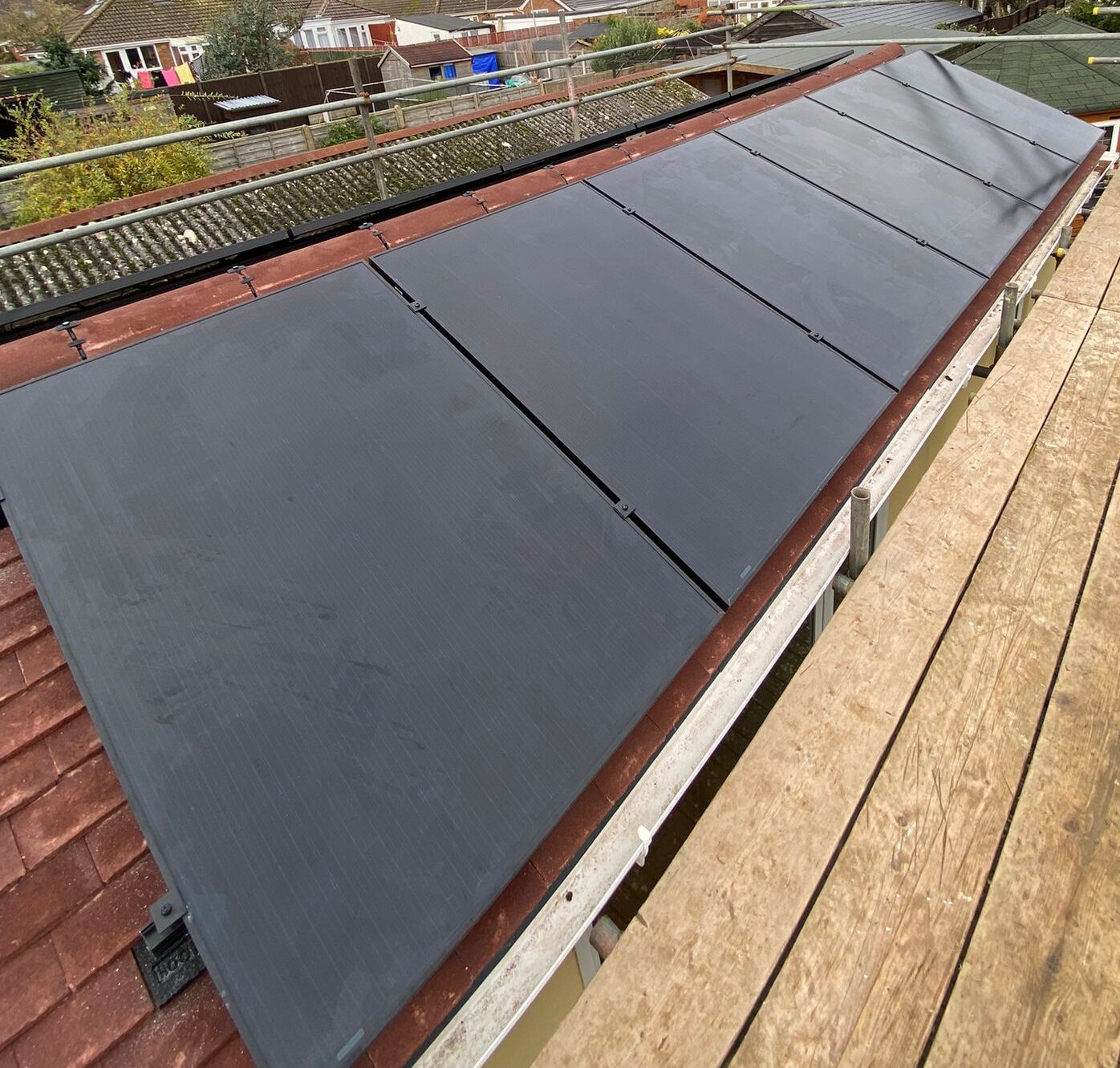

Monocrystalline Solar Panels on a garage roof
Developments in Monocrystalline Technology:
In recent years, there have been several advancements in monocrystalline solar panel technology aimed at improving efficiency, reducing costs, and enhancing performance. Some notable developments include:
- PERC (Passivated Emitter Rear Cell) Technology – PERC technology has become increasingly popular in monocrystalline panels. It involves adding a passivation layer to the rear surface of the solar cell, which reduces electron recombination and improves overall efficiency.
- Bifacial Panels – Bifacial monocrystalline panels have cells that can capture sunlight from both the front and back sides, increasing energy production. These panels are particularly effective in environments with high levels of reflected sunlight, such as snowy or sandy areas.
- Half-Cut Cells – Half-cut monocrystalline cells are divided into two smaller cells, which reduces resistive losses and improves overall efficiency. This design also enhances the panel’s performance in shaded conditions.
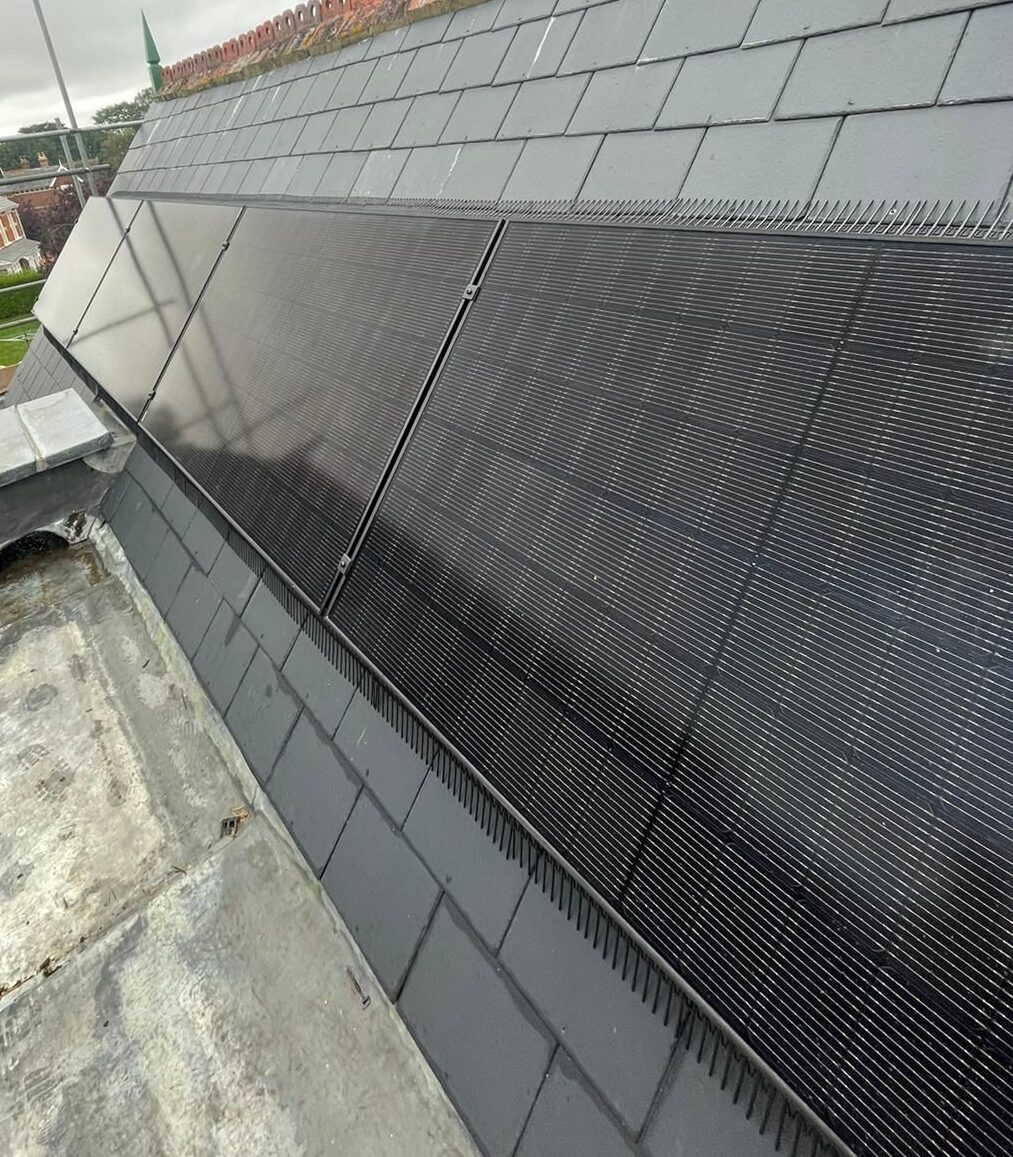

Monocrystalline Solar Panels on a slate roof
Monocrystalline vs. Polycrystalline Panels:
While monocrystalline panels offer several advantages over polycrystalline panels, it’s essential to consider factors such as cost, space availability, and specific energy needs when choosing between the two. Polycrystalline panels may be a more cost-effective option for some installations, particularly those with ample roof space and lower energy requirements.
In conclusion, monocrystalline solar panels represent a cutting-edge technology that continues to evolve and improve. With their high efficiency, space efficiency, and durability, they are an excellent choice for residential, commercial, and utility-scale solar installations, helping to drive the transition towards a cleaner and more sustainable energy future.